Wooden skyscrapers

Introduction
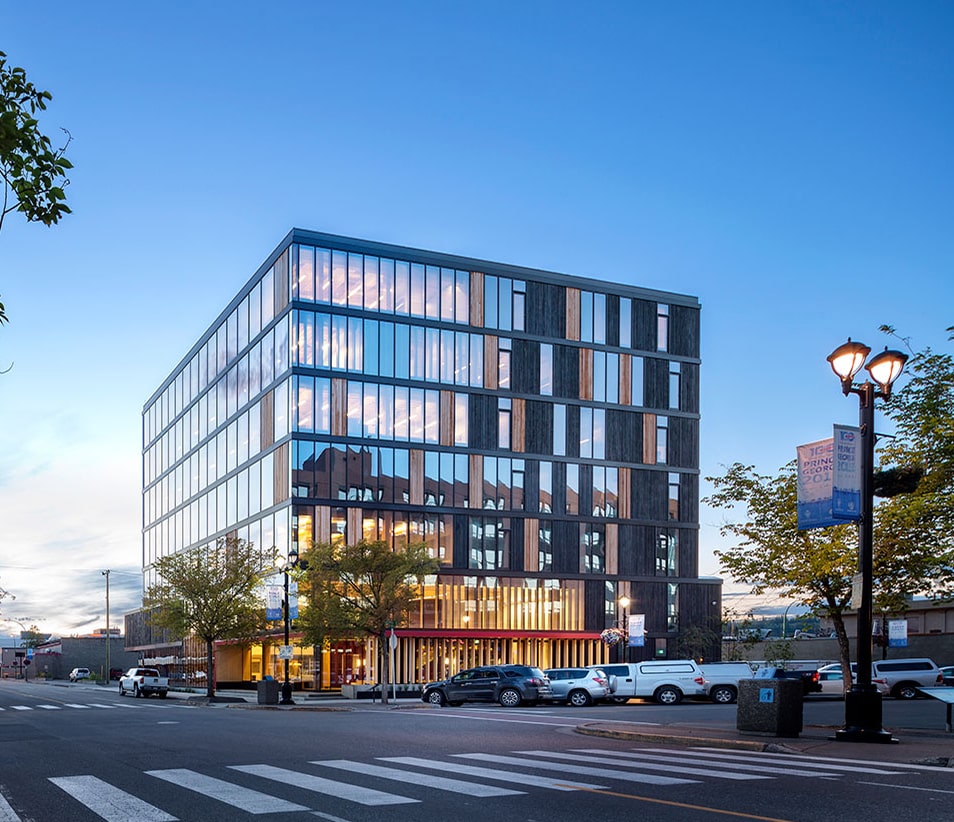
Modern architecture is changing rapidly, and more and more attention is being paid to building materials' environmental friendliness and sustainability. In this context, wooden multi-storey buildings, or so-called timber skyscrapers, are becoming a new trend that could dramatically change the future of urbanism. These innovative buildings not only help to reduce the carbon footprint but also have several other advantages that make them attractive to modern architects and developers.
Why wood?
Wood as a building material has a long history. However, in the context of skyscraper construction, its use has become possible only thanks to new technologies. One of these technologies is cross-laminated timber (CLT). CLT consists of several layers of wooden panels glued together at different angles, ensuring the material's exceptional strength and stability.
This material is strong and lightweight compared to traditional building materials such as concrete or steel. Wooden structures are highly resistant to earthquakes because they are flexible and can absorb energy from seismic waves. In addition, wood is a renewable resource, which makes it environmentally friendly.

Environmental benefits
One of the main reasons why wooden skyscrapers are attracting attention is their environmental friendliness. The production of steel and concrete requires significant energy inputs and emits huge amounts of CO2. Wood, on the other hand, is a natural carbon sink: as trees grow, they actively absorb CO2 from the atmosphere. Once harvested and used in construction, wood continues to retain this carbon, saving it throughout the life cycle of the building. Therefore, the use of wood in construction helps to reduce the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
In addition, the use of wood reduces the energy costs of construction and transportation of materials. All of this makes timber skyscrapers an attractive option for cities seeking to reduce their environmental footprint.
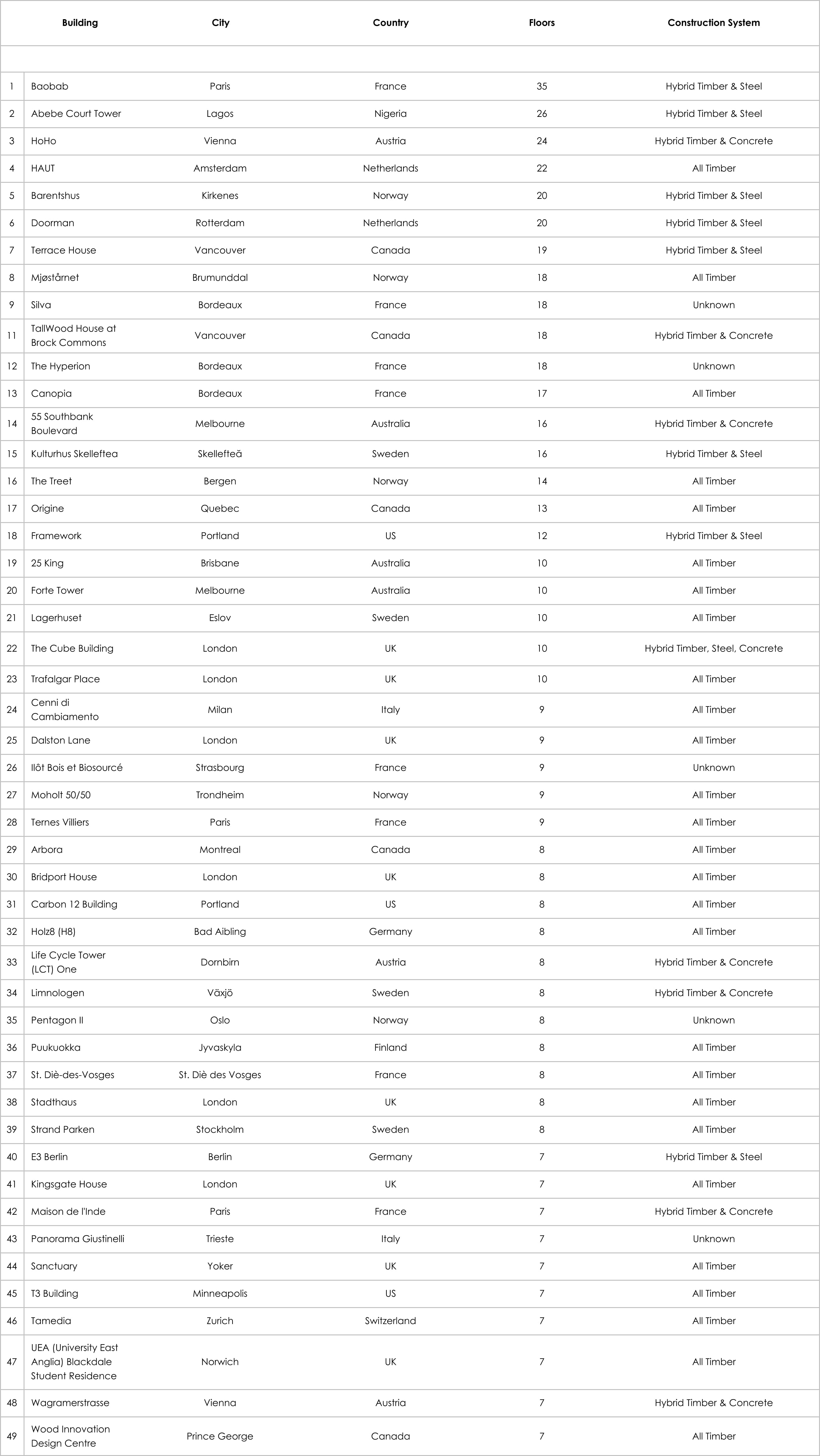
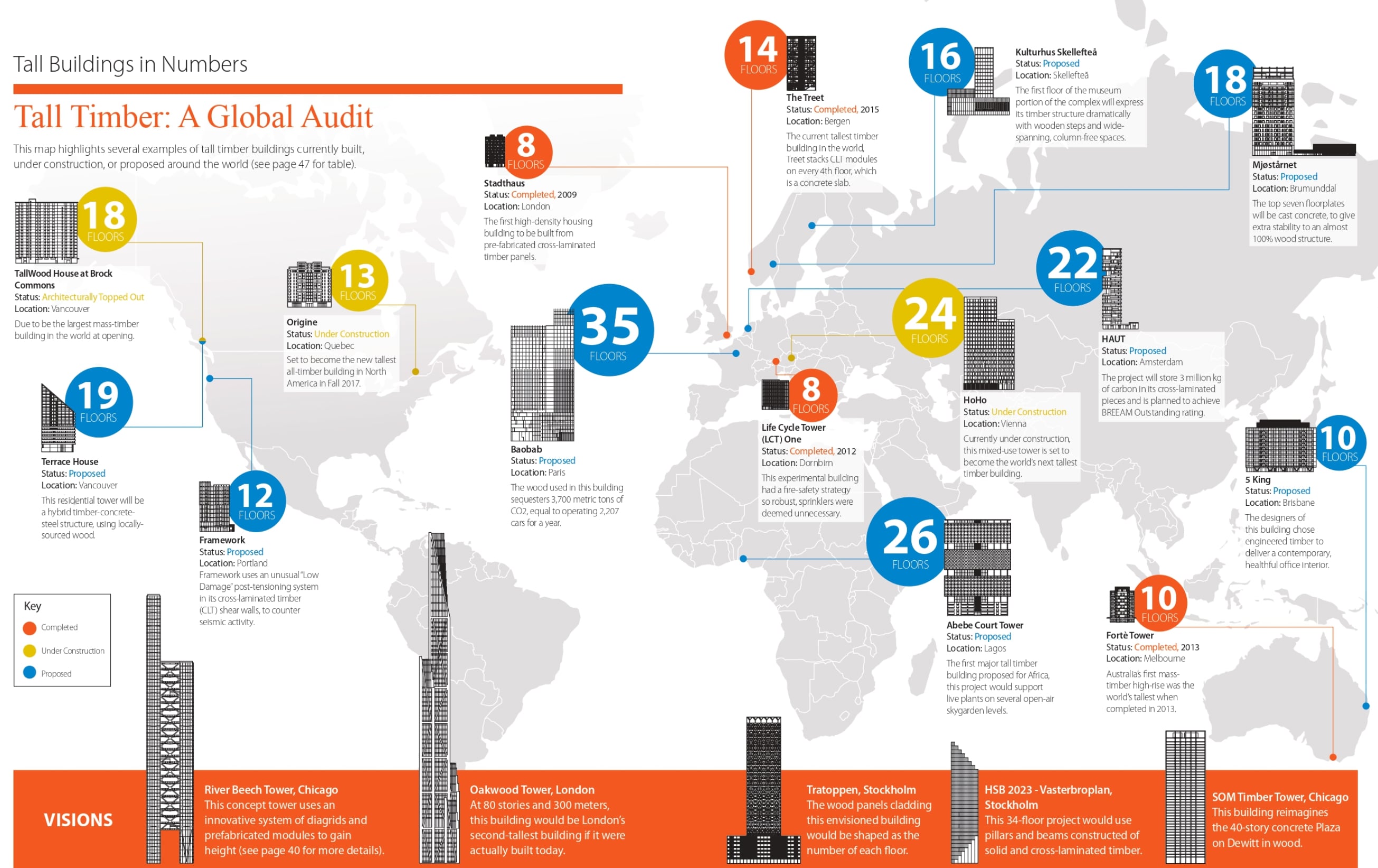
Examples of wooden skyscrapers
Several landmark projects have already been completed and demonstrate the potential of multi-storey wood construction.
HoHo Tower (Vienna, Austria) is one of the tallest wooden buildings in the world, with a height of 84 metres. HoHo Tower has 24 floors and 76% of the materials used are wood. The building has all modern amenities and serves as an example for future wooden skyscraper projects.
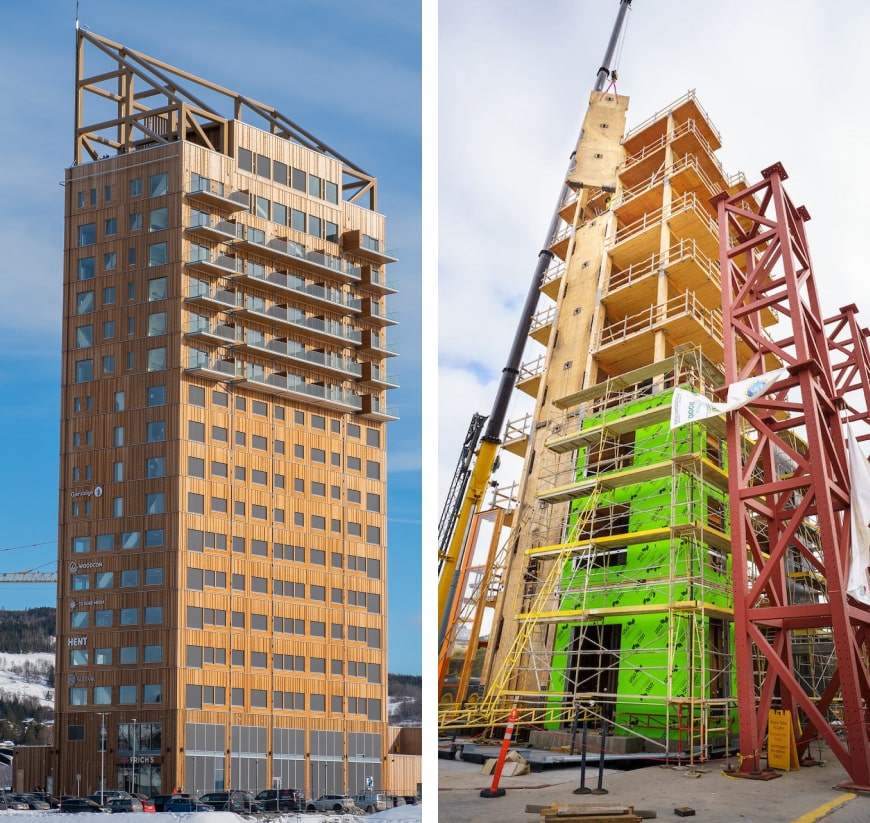
Mjøstårnet (Brumundal, Norway) is the world's tallest wooden skyscraper, 85.4 metres high. It includes a hotel, offices, apartments and a restaurant. The project has been recognised for its eco-friendly approach and innovative use of wood.
Treet (Bergen, Norway) is another example of a successful wooden skyscraper, 49 metres high. It consists of 14 floors and was the tallest wooden building in the world when it was completed in 2015.
Brock Commons Tallwood House (Vancouver, Canada) - a wooden building built on the campus of the University of British Columbia is one of the tallest in the world. This student dormitory has a hybrid construction of steel, concrete and wood.
Origine (Quebec City, Canada) is the Origine residential complex in the Pointe-aux-Lièvres district, which is one of the first wooden high-rise buildings in Canada and is an example of environmentally friendly and sustainable construction.
25 King (Brisbane, Australia) is the tallest commercial timber building in Australia. It is constructed using glulam and cross-laminated timber (CLT), which provides high strength and sustainability.
International House (Sydney, Australia) is the first commercial building in Sydney to be constructed entirely of cross-laminated timber. This project demonstrates the potential of timber structures in modern architecture.
Challenges and the future
Despite their many advantages, wooden skyscrapers face certain challenges. One of them is fire safety. Although modern wood processing technologies significantly reduce the risk of fire, this aspect remains important in the design of such buildings.
Another challenge is regulatory restrictions. In many countries, building codes do not allow for the construction of wooden buildings of such a height, which can be an obstacle to massive multi-storey construction of wood.
However, with the development of technology and changes in design approaches, wooden skyscrapers may become the standard of the future. A kind of building material for the 21st century.
These eco-buildings combine modern design, environmental awareness and innovative solutions, making them attractive to cities around the world.
An example of a future wooden skyscraper is the Marcus Centre, which will potentially become the tallest wooden structure in the world. This ambitious project worth more than USD 700 million envisages the creation of a mixed-use complex that will include up to 750 residential units, office and retail space, hotel rooms and public spaces. The project will be an important part of Milwaukee's development, helping to attract investment and increase the city's population.

Conclusion
Timber skyscrapers are not only a new word in architecture but also a step towards a more sustainable future. By using natural materials and reducing their carbon footprint, these buildings can help preserve the planet for future generations. With the development of woodworking and related technologies, timber skyscrapers have every chance of becoming the new standard in the construction of tall buildings.


Leave your feedback Cancel reply